使网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价
1 ,下一步往右走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j + 1]2 ,下一步往左走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i][j - 1]3 ,下一步往下走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i + 1][j]4 ,下一步往上走,也就是你会从
grid[i][j]走到grid[i - 1][j]m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100
给你一个 m x n 的网格图 grid 。 grid 中每个格子都有一个数字,对应着从该格子出发下一步走的方向。 grid[i][j] 中的数字可能为以下几种情况:
注意网格图中可能会有 无效数字 ,因为它们可能指向 grid 以外的区域。
一开始,你会从最左上角的格子 (0,0) 出发。我们定义一条 有效路径 为从格子 (0,0) 出发,每一步都顺着数字对应方向走,最终在最右下角的格子 (m - 1, n - 1) 结束的路径。有效路径 不需要是最短路径 。
你可以花费 cost = 1 的代价修改一个格子中的数字,但每个格子中的数字 只能修改一次 。
请你返回让网格图至少有一条有效路径的最小代价。
示例 1:

```txt
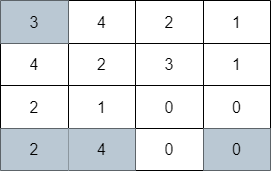
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]]
输出:3
解释:你将从点 (0, 0) 出发。
到达 (3, 3) 的路径为: (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) 花费代价 cost = 1 使方向向下 --> (3, 3)
总花费为 cost = 3.
```
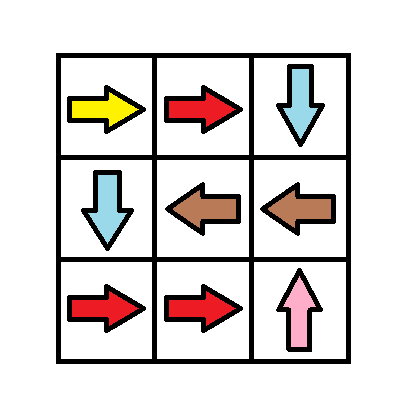
示例 2:
```txt
输入:grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]]
输出:0
解释:不修改任何数字你就可以从 (0, 0) 到达 (2, 2) 。
```
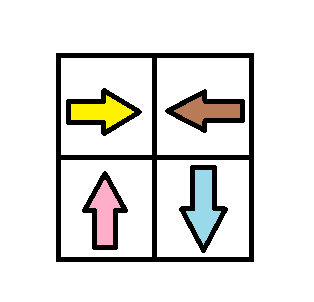
示例 3:
```txt
输入:grid = [[1,2],[4,3]]
输出:1
```
示例 4:
```txt
输入:grid = [[2,2,2],[2,2,2]]
输出:3
```
示例 5:
```txt
输入:grid = [[4]]
输出:0
```
提示: